NET MAUI as a Universal Development Platform


NET MAUI – Let’s Explore What Is It
At the stage of software design, one of the main points is the environment in which the software product will work. It can be a mobile device, a tablet, or a computer running Windows, Linux, or Raspberry PI operating systems. And what if we need a universal environment where we can run our application without being tied to a device? The .NET MAUI platform comes to the aid of the developer. Let’s talk about this in more detail. The abbreviation MAUI stands for Multi-platform App UI. This system is used to develop user interfaces for both classic desktop applications and mobile devices.
Implemented the NET MAUI platform in the form of 2 types of projects:
- Based on Blazor technology.
- Based on XAML technology.
NET MAUI Characteristics
Despite the fact that the system is universal, it still has minimal system characteristics and does not support many outdated devices. Consider the minimum versions of operating systems:
- Android minimum supported version is 5.0 (API 21) if using XAML and Android 6.0(API 23) if we use MAUI Blazor.
- IOS – minimum supported version 10. If we use .NET MAUI Blazor – IOS 11 and above are required.
- MacOS is the minimum version of 10.13. and mandatory use of MAC Catalyst.
- Windows – Microsoft MAUI is available with version 1809 (Windows 10) and Windows 11 is supported.
- Linux – at the moment it is known that there is support, but there are no minimum system requirements.
From this characteristic, we can notice that the Blazor variant is more demanding on operating systems. If we consider support for Linux systems, and this will work well, this opens up great opportunities for using the MAUI App on other devices, including TVs and projectors. MAUI developers get great development opportunities – code once – works everywhere.
Features of .NET MAUI Technology
A nice feature for MAUI developers is that this system supports hot reloading .NET. What does this mean? This is a feature that allows you to change the program code while the application is running without having to recompile and stop it. Everything happens in real time.
Also, for the convenience of developers, there is access to API and tools for a specific platform. This allows the use of sensors such as a compass, gyroscope, and accelerometer. It is also possible to receive complete information about the device – the level of connection with the Internet.
How the MAUI Architecture Works
Consider the architecture of this technology based on the image provided by Microsoft:
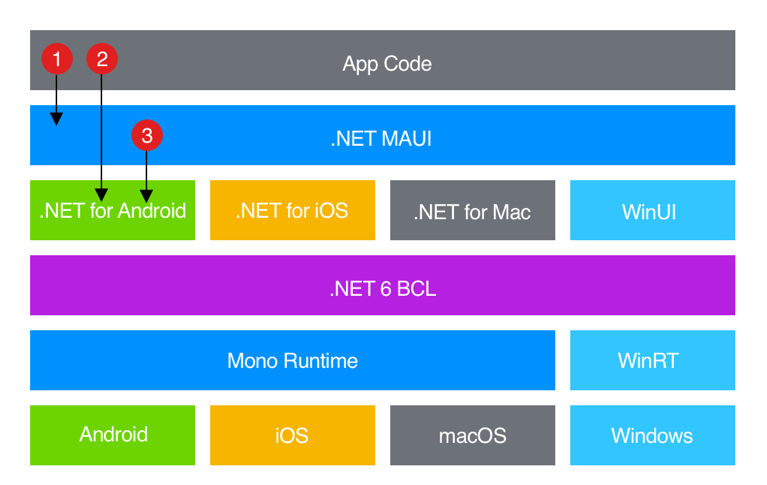
Consider the sequence of code execution.
When running the code, our code interacts directly with the MAUI API. Next MAUI uses its API to use the target platform interface, however, the application code can use the API of the target platform function directly.
Next, consider compiling for each operating system:
- Android – Compilation is from C# to Intermediate Language (IL) then JIT compilation to native assembly.
- IOS – compilation happens immediately to ARM assembly code
- macOS – compile as under IOS with subsequent changes using the Mac Catalyst program
- Windows – uses the WinUI 3 library to create a ready-made windows maui apps
Comparison of NET MAUI with Other Technologies
At the moment, the main contender for comparison is Xamarin. For a more detailed comparison, consider this technology.
Xamarin is an open-source technology that allows you to create high-performance applications on different architectures at a level of abstraction that allows you to provide control between the main code and the code of the underlying platform, being a link. Does it sound familiar? The question arises: why then should we use NET MAUI? This platform is an evolution of Xamarin Forms – no need to create different projects, 1 project for all operating systems. There is no need to change the logic moving away from the operating system, there is no dependency on the file system either.
Let’s Summarize
In this article, we examined the main features of the new progressive technology by Microsoft – .NET MAUI. This technology makes it possible to significantly facilitate the development of software, at the moment when the project is simultaneously needed on different operating systems and devices: phones, computers, tablets, and even TVs.










Recent Comments