
“Cook” Your Software Impressively Using Agile Sprints! | KoderShop

Sprints in Agile project management: what are they and how to plan them
Any more or less complex topic is always better to analyze on a simple and understandable example. The field of software development operates with a lot of terms and concepts that will not always be obvious to the average user of the same software, even if they are very easy to understand if you delve a little into the topic. In this article, we will explain in simple terms what is a sprint in Agile software development, and tell what the Scrum approach has to do with it.
Agile in a nutshell
To begin with, let’s imagine that you came to a restaurant and ordered five different dishes at once for a large company. In this analogy, you are the customer of the project, and the restaurant kitchen is its performer. If you ordered only one dish, the best solution for the contractor would be to apply the classic cascade project management method (waterfall): prepare the necessary set of products → cook the dish → put it on a plate beautifully → serve.
However, we are talking about five menu items at once. This formulation of the task requires a slightly different approach, since with the cascade method each time you have to wait until one dish is cooked before starting to cook another. This is where the Agile project management method comes into play. It involves dividing a project not into phases, but into smaller projects that are executed in parallel. The iterations of these subprojects are what we call sprints. At the same time, upon completion of each sprint, all plans and requirements are tested for relevance and expediency given the results already obtained.
Put your finger on the pulse and trust: the benefits of Agile
The main advantage of Agile is that the team releases the product in batches, which allows them to respond in time to end-user feedback, market trends, etc., without violating plans for months ahead.
Agile principles focus not on indicators, but on people and their natural interaction in solving certain problems. This allows agile-team members to decide for themselves which way to accomplish the task will be most effective. As practice shows, by placing such responsibility on the project executors, companies achieve greater success, because, understanding the level of trust shown, employees make every effort to justify it.
The mistake
So, we have already said what is sprint in Agile methodology: a kind of iteration of a subproject. More specifically, this is a fixed time period in which the team completes a certain piece of a global task (whereas iteration is understood not as a period, but as a piece of work itself). But we did not specify that in the Manifesto for Agile software development, which gave the name to the whole concept, sprints are not even mentioned.
For ease of understanding, project management methods such as Scrum or Kanban are often identified with Agile. However, this is a mistake. In its essence, Agile is not a method, but a set of principles that became the basis for the formation of the aforementioned Scrum and Kanban methods.
Moreover, sprints are inherent just in Scrum, while in Kanban the process is not interrupted (we will talk about this some other time). So, the correct wording of the question is not “what are sprints in agile?”, but “what are sprints in scrum?”
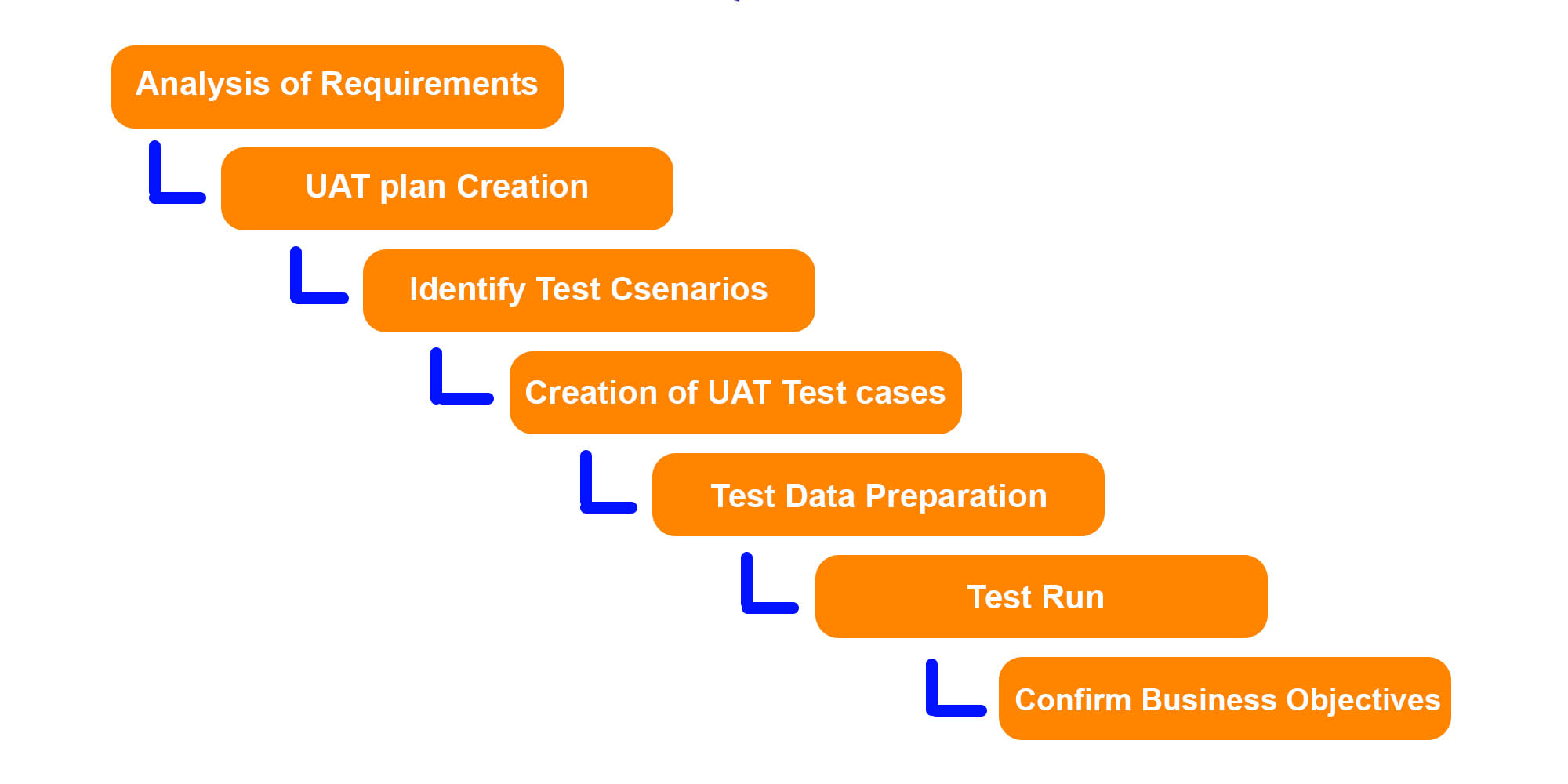
How to plan and implement a sprint cycle in software engineering?
Well, we have another term here – the sprint cycle. And that’s one more thing you need to know. A sprint cycle is usually understood as the sequence of such sprint stages in Scrum:
- Sprint planning
- Daily scrum
- Sprint review
- Sprint retrospective
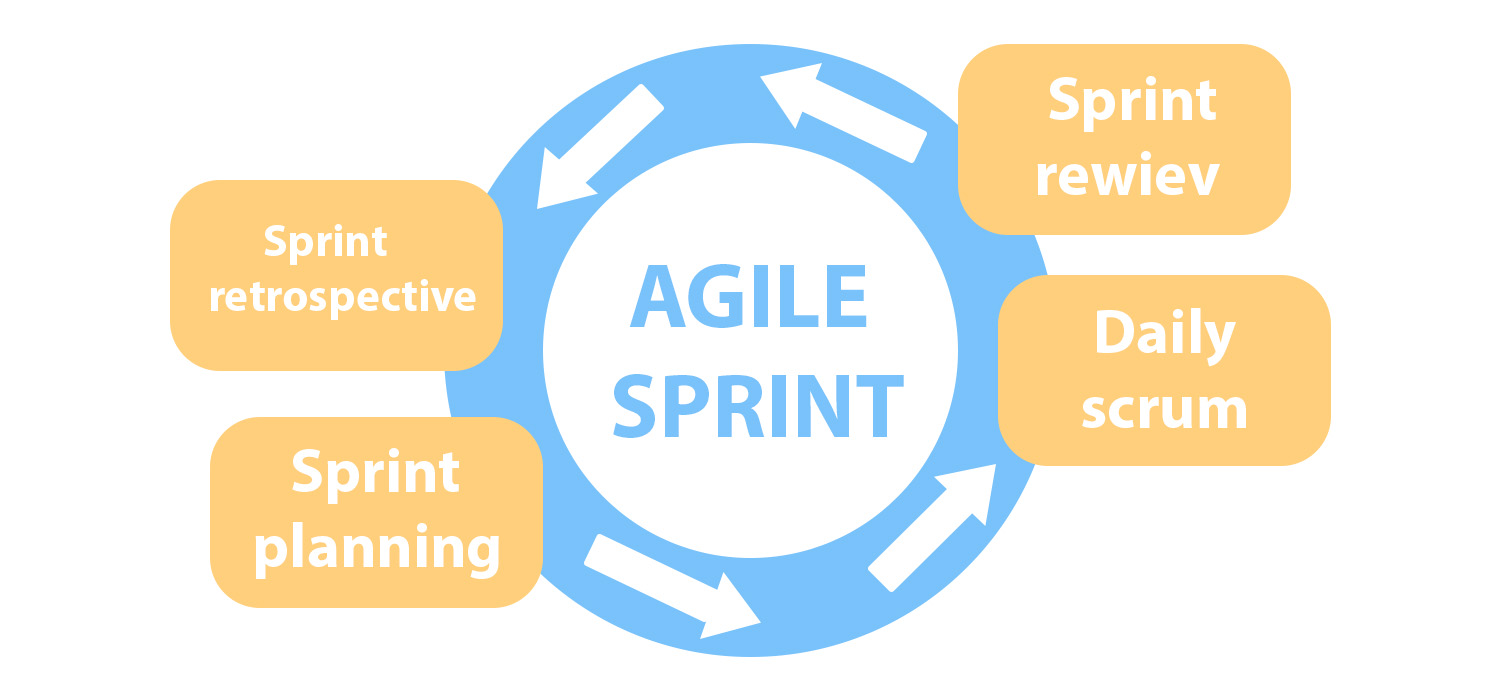
Sprint planning involves a meeting in which the team is expected to answer two fundamental questions: what kind of work needs to be done within this sprint and how particularly this work should be done. The product developers` team, its owner (customer), and Scrum master are involved in this process. Together they bring out the definition of the sprint goal as well as the sprint tasks from the product backlog that needs to be done until the sprint is ended. When this is done, the developers sketch out the sprint plan. Thus, the sprint backlog is formed.
Daily scrums are daily discussions that are necessary for the timely analysis of the results of the work done and the quick identification of possible difficulties during the sprint.
A sprint review is needed to summarize the work done. At such meetings, team members show what was done and how, clarify the details, test the functionality of the product (or some parts of it), and share their opinion about the already implemented software features. That is, it is assumed that the team already has some demos by the sprint review.
For such a meeting to be fruitful, it is necessary to clearly formulate the criteria for product readiness. Most often, this is done during sprint planning, but in rare cases, the team may determine the readiness criteria as the work progresses.
Do not confuse the sprint retrospective with the sprint review. During the retro, no one analyzes the results of the sprint. Instead, the team discusses which areas need to be refined and improved in the next iteration. To some extent, the retrospective definition in Scrum is a preparatory stage for planning the next sprint.
As you can see, the sprint methodology in Scrum is not as difficult to understand as it might seem at first glance. Of course, by introducing the Scrum approach or any other direction of Agile into the workflow of your enterprise, you are unlikely to be able to immediately avoid all the difficulties. But this game is worth the candle. The main thing when implementing Agile is the correct selection of a team, and everything else will work out quickly enough.
FAQ
What is sprint backlog in Agile?
In Scrum model the sprint backlog presented as a list of tasks that the development team must complete during this sprint. It also includes a pre-designed plan according to which the performers will do the work.
What`s the difference between sprint backlog and product backlog?
Unlike a sprint backlog, a product backlog contains a list of all the tasks in a project. In the product backlog, tasks are described in order of importance, but Agile principles do not require strict adherence to this order (of course, this may vary depending on the specifics of the project). In the process of work, the team itself determines which task is more appropriate to perform at one time or another.
The basis for the formation of the product backlog is the so-called roadmaps (a document that describes the strategy for the development of your product in the long term), as well as the requirements for the product, which we have already written about here. The product backlog usually serves as the basis for the sprint backlog when it is planned.
How long is a sprint in Agile?
The Manifesto for Agile does not specify the duration of the sprint. However, typically Scrum development teams set a sprint timeframe of one to four weeks. Most often, an agile sprint lasts two weeks.











Recent Comments