Overview
By adding automation to the various stages of app development, CI/CD is a technique for regularly delivering apps to clients. Continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment are the three core CI/CD concepts. The challenges integrating new code can provide for development and operations teams are addressed by CI/CD (AKA “integration hell”).
In particular, CI/CD brings continuous monitoring and continual automation throughout the whole lifespan of an app, from the integration and testing stages to the delivery and deployment stages. Development and operations teams collaborate in an agile manner using either a DevOps or site reliability engineering (SRE) methodology, and these interconnected processes are collectively referred to as a “CI/CD pipeline tools.”
Differences Between CI and CD?
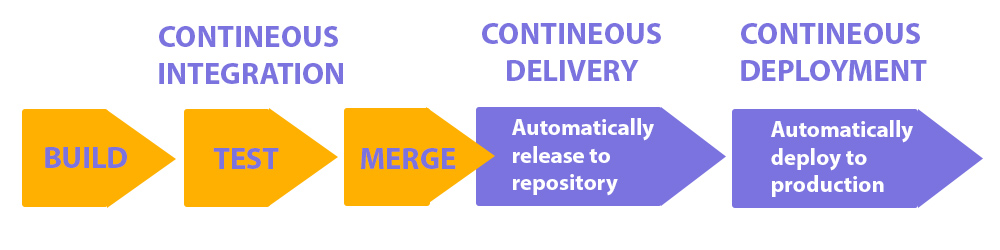
There are numerous definitions for the abbreviation CI/CD. Continuous integration is always referred to as “CI” in CI/CD, and it is a method that automates development. A successful CI involves routinely building, testing, and merging new code changes to an app into a shared repository. It offers a solution to the issue of having too many potentially incompatible branches of an app in development at once.
Continuous delivery and/or continuous deployment are similar ideas that are occasionally used interchangeably and are denoted by the “CD” in “CI/CD.” Both are concerned with automating pipeline steps after the initial stages, however they are occasionally used independently to highlight the extent of automation.
Continuous delivery typically entails that an operations team can deploy a developer’s changes to a live production environment after they have been automatically checked for bugs and submitted to a repository (such as GitHub or a container registry). It provides a solution to the issue of the development and business teams’ limited visibility and communication. In order to ensure that deploying new code requires the least amount of work possible, continuous delivery was created.
The alternative meaning of “CD” is continuous deployment, which is the process of automatically pushing changes made by developers from the repository to a live environment where users can access them. It deals with the issue of operations teams being overburdened with manual tasks that impede app delivery. By automating the following pipeline stage, it expands on the advantages of continuous delivery.
Both the connected practices of continuous integration and continuous delivery, as well as all three connected practices of continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment, may be referred to as CI/CD. It gets even more difficult because “continuous delivery” is occasionally used to refer to continuous deployment procedures as well.
In the end, it’s probably not worth your time to get mired in these semantics; instead, just keep in mind that CI/CD is truly a process that adds a high level of ongoing automation and continuous monitoring to app development. This process is frequently represented as a pipeline.
Depending on how much automation has been incorporated into the CI/CD pipeline, each situation will determine what the terms mean. Many businesses begin by using CI, and as time goes on, they go toward automating delivery and deployment, for example as part of cloud-native apps.
Our specialists can assist your company in creating the cultures, tools, and practices required to create new apps and upgrade old ones in a more effective manner.
Continuous Integration
The objective of contemporary application development is to have numerous developers working on various aspects of the same app concurrently. The effort that results, however, can be laborious, manual, and time-consuming if an organization is set up to combine all branching source code together on one day (known as “merge day”). This is so that modifications made to an application by a developer working alone won’t necessarily conflict with other changes being made to the same application at the same time. Instead of the team deciding on a single cloud-based IDE, this issue may be made worse if each developer has customized their own local integrated development environment (IDE).
Continuous Delivery
Continuous delivery automates the deployment of that validated code to a repository after the automation of builds and unit and integration testing in CI. Therefore, it’s critical that CI be already included in your development pipeline in order to have a successful continuous delivery process. A codebase that is constantly prepared for deployment to a production environment is the aim of continuous delivery.
Every step in continuous delivery—from merging code changes to delivering builds fit for production—involves test automation and code release automation. The operations team can then swiftly and easily deploy an app to production after that procedure is complete.
Continuous Deployment
Continuous deployment is the last phase of an advanced CI/CD process. Continuous deployment automates the release of an app to production as an extension of continuous delivery, which automates the release of a production-ready build to a code repository. Continuous deployment largely relies on well-designed test automation since there is no manual gate at the pipeline level prior to production.
Continuous deployment actually allows a developer’s modification to a cloud application to go live minutes after it is written (assuming it passes automated testing). It is now much simpler to regularly gather and take into account customer feedback. When all of these related CI/CD techniques are used, deployment of an application becomes less hazardous, making it simpler to release app modifications incrementally rather than all at once. A significant upfront investment is also required because a number of testing and release phases in the CI/CD pipeline need the creation of automated tests.
CI/CD Tools List
What are Ci/CD tools?
A team can automate development, deployment, and testing with the aid of CI/CD systems. Some technologies specialize in continuous testing or related tasks, while others manage development and deployment (CD) and the integration (CI) side.
Lets start and present the 14 best and most used CI/CD tools.
Without separating CD tools from CI tools the below list includes 7 of each of the categories.
Jenkins, an open source automation server, is one of the most well-known CI/CD systems. Jenkins can manage everything from a straightforward CI server to a full-fledged CD hub.
1. Jenkins

The central build and continuous integration process is carried out by Jenkins, an open-source automation server. It is a standalone Java program providing packages for Windows, macOS, and other operating systems that resemble Unix. Jenkins allows creating, delivering, and automating for software development projects and has hundreds of plugins available.
Jenkins key features:
- Straightforward OS installation and upgrading
- A straightforward and user-friendly interface
- Large community-contributed plugin resource makes it extensible
- Simple environment setup through the user interface
- Supports master-slave architecture and distributed builds
- Create schedules using expressions
- Supports pre-build steps that use shells and Windows command execution.
- Offers support for notifications about build status.
License: Free.
2. CircleCI

A CI/CD technology called CircleCI promotes quick software development and publication. The user’s pipeline can be automated with CircleCI, from code development to testing and deployment.
To make builds when new code lines are committed, CircleCI may be integrated with GitHub, GitHub Enterprise, and Bitbucket. CircleCI also offers cloud-managed continuous integration hosting or use local infrastructure that is protected by a firewall.
CircleCI key features:
- Integrates with GitHub Enterprise, Bitbucket, and GitHub
- utilizes a virtual machine or container to run builds
- Simple bug fixing
- Automatically parallelizing
- Rapid tests
- Individual emails and IM notices
- Branch-specific deployment that is ongoing
- highly adaptable
- Custom commands and automated merging for package uploading
- Quick setup and limitless creations
License: Starting with Linux plans, one job can be executed without parallel processing with no additional cost. You can choose the plan(s) you require after viewing the cost throughout the signup process.
3. TeamCity

JetBrains’ build management and continuous integration server is called TeamCity.
A continuous integration solution called TeamCity aids in developing and deploying various project kinds. TeamCity interacts with Visual Studio and IDEs and operates in a Java context. The program supports.NET and open-stack applications and may be installed on both Windows and Linux systems.
New UI and direct connection with GitLab are features of TeamCity 2021.1 . Additionally, GitLab and Bitbucket server pull requests are supported. The release contains requests for AWS Spot Fleet, detection of Go tests, and token-based authentication.
TeamCity key features:
- Provide many options for reusing the settings and configurations of the parent project in the child project
- Simultaneously does parallel builds in various contexts.
- Makes it possible to run previous builds, see test history reports, pin, tag, and favorite builds.
- Simple to interact with, alter, and expand the server
- ensures the CI server is operational and reliable
- Flexible user administration, user roles assignment, grouping of users, several user authentication methods, and a log of all user activity for full transparency of all server activities
License: A commercial tool with both open-source and exclusive licensing is TeamCity.
4. Bamboo

A continuous delivery pipeline is created by Bamboo, a continuous integration server, which automates the management of software application releases. Assigning versions, categorizing releases, delivering, and activating new versions on production are all covered by Bamboo.
Bamboo key features:
- Up to 100 remote build agents are supported
- Parallelize test runs and receive fast feedback.
- Generating photos and submitting them to a repository
- Per-environment rights that let developers and testers deploy to individual environments as needed while the production environment is kept secure
- Detects new branches in repositories for Git, Mercurial, and SVN and automatically applies the main line’s CI scheme to them.
- Builds are triggered based on changes found in the repository. Notifications are pushed from Bitbucket, according to a predetermined schedule, when a build is finished, or any combination of these.
License: Instead of using users, Bamboo bases its pricing levels on agents or “build slaves.” More processes can run simultaneously, either in the same build or in multiple builds, the more agents there are.
5. GitLab

GitLab is a collection of instruments for controlling various phases of the software development lifecycle. The main offering is a Git repository manager for the web with tools for issue tracking, analytics, and a wiki.
With each commit or push in GitLab, you have the option to start builds, launch tests, and deploy code. Jobs can be created on another server, in a virtual machine, or using Docker containers.
GitLab key features:
- Branching tools are used to see, produce, and manage codes and project data.
- Using a single distributed version control system, create, develop, and manage code and project data to enable quick iteration and the delivery of business values.
- Offers scalability and a single source of truth for working together on projects and code
- Automates builds, integration, and source code verification to assist delivery teams in embracing CI.
- Delivers safe applications and licensing compliance with container scanning, static application security testing (SAST), dynamic application security testing (DAST), and dependency scanning.
- Aids in automating and accelerating application delivery and releases.
License: GitLab is a for-profit product and free download. It provides hosting for SaaS on GitLab, your own instance on-premises, in the public cloud, or both.
6. Buddy

Buddy is a CI/CD tool that uses code from GitHub, Bitbucket, and GitLab to build, test, and deploy websites and applications. It uses DevOps, monitoring, and notification processes along with Docker containers that come pre-installed with the languages and frameworks that may be built upon.
Buddy key features:
- Easy to modify Images created using Docker as a test environment
- Intelligent change detection, cutting-edge caching, parallelism, and general optimizations
- Create, alter, and utilize test and build environments
- Workspace, project, pipeline, and action scopes are fixed and programmable, plain and encrypted.
- Elastic, MariaDB, Memcached, Mongo, PostgreSQL, RabbitMQ, Redis, Selenium Chrome, and Firefox are examples of attachable services.
- Monitor with infinite history, real-time progress, and logs
- Workflow management using templates for pipeline cloning, exporting, and importing
- Superior Git integrations and support
License: Buddy is a freely available.
7. Travis CI

A CI service used to build and test projects is called Travis CI. New commits are automatically found by Travis CI and pushed to a GitHub repository. Additionally, Travis CI will build the project and run tests after each new code commit.
Numerous build configurations and languages, including Node, PHP, Python, Java, and Perl, are supported by the tool.
Travis CI key features:
- Rapid setup
- Views of live builds for GitHub projects
- Pull request assistance
- Multiple cloud services deployment
- Built-in database services
- Auto-deploys when builds pass
- Pristine VMs for each build
- Complies with iOS, Linux, and macOS
- Supports a variety of languages, including R, C, Python, Ruby, Java, C, C#, C++, Perl, PHP, and JavaScript (with Node.js).
License: A hosted CI/CD service is Travis CI. On Travis-CI.com, test runs for personal projects are available for a charge. On Travis-ci.org, open-source projects can be applied for free.
8. Codeship

A hosted platform called Codeship allows for many early and automatic software releases. By streamlining the testing and release procedures, it aids software firms in producing better products more quickly.
Codeship key features:
- Integrates with a variety of tools, services, and cloud computing environments.
- Simple to use gives developers prompt, detailed help.
- With CodeShip’s turnkey infrastructure and straightforward UI, builds and deploys are completed more quickly.
- Option to choose the size, CPU, and memory of an AWS instance
- creates teams and assigns access to team members and organizations using the notification center
- Project dashboards, intelligent notification management, and seamless third-party interfaces all work together to give you a high-level picture of your projects’ status.
License: Utilize 100 builds each month for no cost; unlimited builds are available for $49 per month. With bigger instance sizes, you can pay for additional parallel pipelines or concurrent builds.
9. GoCD

GoCD is an open-source development and software release solution from ThoughtWorks that supports contemporary infrastructure on CI/CD.
GoCD key features:
- Dependencies are simple to configure for quick feedback and on-demand deployments.
- Favors reliable artifacts: A specific changeset serves as the anchor for each pipeline instance.
- Controls your whole workflow, allowing you to trace changes from committing to deployment at a look.
- The upstream and downstream are clearly visible.
- Any version may be used at any time.
- allows you to distribute any known-good version of your application to any location you want.
- Utilizes the Compare Builds functionality to obtain a straightforward bill of materials for any deployment.
- Keeps configuration organized by leveraging the GoCD template system to reuse pipeline setups.
- There are already many plugins available
License: Free and open-source.
10. Wercker

Developers that are working with or considering beginning a new project based on Docker may find Wercker to be a good fit. Wercker assists businesses in using CI/CD, microservices, and Docker with their development teams.
Oracle disclosed that it had finalized a deal to acquire Wercker on April 17, 2017.
Wercker key features:
- Version control and integrations with Git, including GitHub, Bitbucket, and GitLab
- Make a local copy of the SaaS environment using Wercker CLI to test and troubleshoot pipelines before deploying.
- Supports Wercker’s Docker integration helps create small containers with manageable sizes.
- You can interact with notifications through Walterbot, a chatbot in Wercker, to find out the status of the development.
- Environment variables aid in preventing the repository from storing sensitive data.
- Wercker makes advantage of essential security features, such as source code protection to disable test logs, protected environment variables, and user and project permissions that are customisable.
License: Following its acquisition, Oracle did not disclose Wercker’s pricing.
11. Semaphore

A hosted CI/CD solution for testing and deploying software projects is called Semaphore. Through a development process based on pull requests, Semaphore sets CI/CD standards.
Semaphore key features:
- Connected to GitHub
- Automates any pipeline for continuous delivery
- Use the quickest CI/CD platform
- Scales your project automatically so that you only pay for what you really need Native Docker support. Applications built with Docker are tested and released.
- Offers Boosters, a feature for Ruby projects that automatically parallelizes builds to cut down on the time it takes to execute the test suite.
License: Flexible. The capacity of your package determines your options for typical CI services. Semaphore 2.0 will scale in the interim based on your team’s actual requirements, so you won’t be charged if you don’t use the product.
12. Nevercode

For mobile apps, Nevercode offers CI/CD. Faster native and cross-platform app development, testing, and publication are all benefits.
Nevercode key features:
- Automatic setup and configuration
- Test automation includes code analysis, real-world testing on devices, unit and UI testing, and parallel testing.
- Automatic publishing: Crashlytics, TestFairy, Google Play, and HockeyApp
- A thorough summary of your build and test status
License: Flexible. Different continuous integration plans for various needs. Standard plans are available, or you can ask for a plan that is specially created for your needs.
13. Spinnaker

AWS EC2, Kubernetes, Google Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, Google App Engine, etc. are just a few of the cloud providers that Spinnaker supports for releasing and deploying software changes across.
Spinnaker key features:
- Creates deployment pipelines that launch and stop server groups, conduct integration and system tests, and keep track of rollouts. Git events, Jenkins, Travis CI, Docker, cron, or other Spinnaker pipelines can all be used to start pipelines.
- Create and deploy immutable images to accelerate rollouts, make rollbacks simpler, and get rid of configuration drift problems that are difficult to troubleshoot.
- Use the metrics provided by monitoring services like Datadog, Prometheus, Stackdriver, or SignalFx to connect your releases and use canary analysis.
- With Halyard, Spinnaker’s CLI administration tool, you can install, configure, and upgrade your instances.
- Set up SMS, Slack, HipChat, or email event notifications (via Twilio)
License: Open source.
14. BuildBot

Buildbot is a “Python-based CI framework” that automatically rebuilds and tests the source tree after each change while automating the compile and test cycles to validate code changes. As a result, construction issues are rapidly identified.
BuildBot key features:
- Automate build processes, application deployment, and the control of complex software-release procedures.
- Supports rich status reporting, flexible connection with version-control systems, distributed, parallel execution across different platforms, and
- Executes builds on several slave platforms.
- Arbitrary build process and handles C and Python programs
- Python and Twisted are the minimum host requirements.
License: Open source.
Conclusion
The top 14 CI/CD tools on this list are the ones that are currently selling the best. We hope this list has given you enough information to make an informed decision about the program that best meets your needs. The CI/CD tools listed below are the most developed ones with the crucial features for your projects. Your final decision will be influenced by your needs, the infrastructure that is in place, as well as opportunity for improvement in the future.
The CI/CD and DevOps trends will keep changing, giving the market room to expand and advance. This list will be updated to guarantee that the information is accurate for you as the environment changes. Additionally, Katalon Academy is offering you a free course to assist you learn more about the CI/CD pipeline.
You can also use this free self-assessment to find out where your team stands in the continuous testing maturity roadmap and to receive professional advice on how to enhance your CI/CD.