In many operational environments, business processes do not start in the ERP system but on the shop floor, at packing stations, or at the checkout counter. Employees scan products, press buttons, weigh items, or complete manual steps long before the corresponding action is recorded in software. When this connection between physical work and digital records is weak, even well-designed workflows in Odoo rely heavily on manual input and delayed updates. This is where the Odoo IoT Box, also known as Odoo IoTBox or IoTBox Odoo, becomes relevant, linking physical actions directly to Odoo business processes.
The Odoo IoT concept, often described as IoT in a box, focuses on turning simple device interactions into system actions. Instead of switching back and forth between equipment and computer screens, operators can trigger predefined steps in Odoo through scanners, buttons, or measurement devices connected via IoT boxes. The IoT Box itself does not manage workflows or business rules. Instead, it only delivers device signals to Odoo 19, where standard modules process them as part of normal business operations. In this way, IoT in Odoo helps reduce unnecessary manual input while keeping process control fully inside the ERP system.
This guide explains how the Odoo IoT Box integrates with core applications such as Manufacturing, Quality, Inventory, and Point of Sale, and how Odoo wireless and network-connected devices can support faster and more reliable execution of daily tasks.
How Odoo IoT Box Works: From Device Signal to Business Action
The Odoo IoT Box, also called Odoo IoTBox or IoTBox Odoo, connects physical devices directly to Odoo business processes. Instead of manually entering data from scanners, scales, printers, or buttons, device signals are automatically sent to Odoo, where workflows in modules like Inventory, Manufacturing, or Point of Sale process them. This approach reduces errors, saves time, and ensures that physical operations are accurately reflected in the ERP system. IoT in a box setups make it easy to manage multiple devices through a single Odoo box, while Odoo wireless connectivity and operational IoT subscriptions expand flexibility and monitoring capabilities.
What IoT in a Box Means in the Odoo Architecture
The concept of IoT in a box refers to a preconfigured hardware gateway that supports multiple device types through a single connection point. Rather than integrating each scanner, scale, or printer separately, companies deploy one Odoo IoT Box per workstation or area. This approach reduces network complexity and centralizes hardware communication. For system administrators, it also means that device drivers, protocols, and updates are handled at the Odoo IoTbox level instead of across multiple machines.
How Odoo IoT Processes Device Signals Inside Applications
It is important to understand that Odoo IoT does not control business decisions. The IoT box Odoo only delivers device signals, while actual processing happens inside standard Odoo modules. For example, a barcode scan may validate a stock move, a scale reading may confirm production output, or a button press may approve a quality step. All permissions, validations, and automation rules remain part of IoT Odoo workflows configured in the ERP, not in the hardware layer.
Odoo Wireless Devices and Network Connectivity
Most devices connected through the Odoo IoT Box communicate wirelessly over the local network. This reduces the need for physical cabling and allows flexible workstation layouts in warehouses, production areas, and retail environments. Wireless connectivity also makes it easier to move or replace devices without reconfiguring Odoo itself. As long as the equipment can communicate with the Odoo IoT Box, it can participate in IoT-enabled workflows.
IoT Subscription and Device Management Interfaces
Some advanced integrations and cloud-based services may require an IoT subscription, depending on the deployment model and device ecosystem. Within Odoo 19, connected hardware can be monitored and managed through interfaces such as “IoT in a Box – My Devices”, which provides visibility into device status and connectivity. This allows teams to detect offline equipment quickly and maintain stable operations without manual troubleshooting on each workstation.
Odoo IoT Box Explained: From Initial Setup to Device Integration
After physically connecting and powering on the IoT Box, the software setup in Odoo begins with configuring the IoT module and device management settings. Before physical devices can send signals to Odoo, the system must define how Odoo IoT boxes will connect to equipment, handle events, and interact with business workflows. These foundational settings ensure that device signals are accurately recorded in Odoo modules such as Inventory, Manufacturing, or Point of Sale, while maintaining consistent processes and avoiding errors. By establishing a structured setup at the start, companies create a stable environment where IoT in a box solutions improve operational efficiency without introducing unnecessary complexity.
- First, activate the Odoo IoT Box module from the application menu, as shown in the screenshot. Once activated, the IoT functionality becomes available in the system.

- After activation, proceed to the main device configuration by clicking the “Connect” button in the IoT Boxes interface. This opens the setup wizard where devices can be registered, tested, and linked to specific workflows.
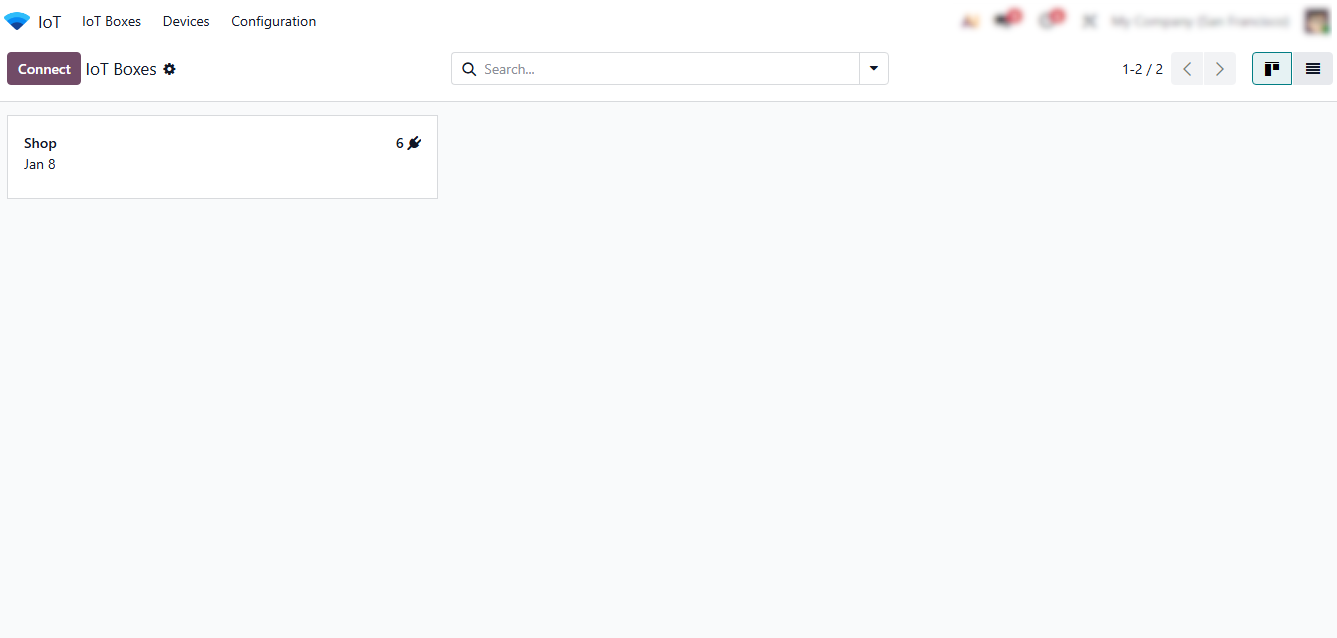
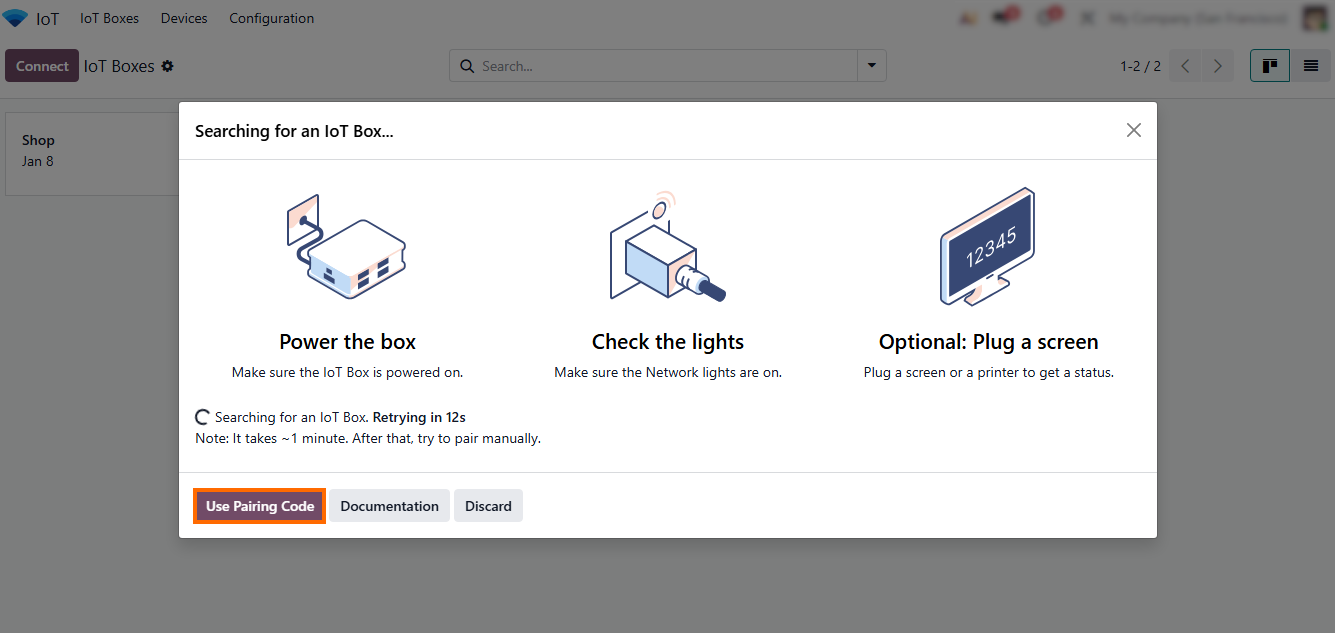
- Click “Connect” to add a new device and wait for the system to automatically start searching for an IoT Box. Alternatively, click “Use Pairing Code” to manually link a device by entering its unique code.
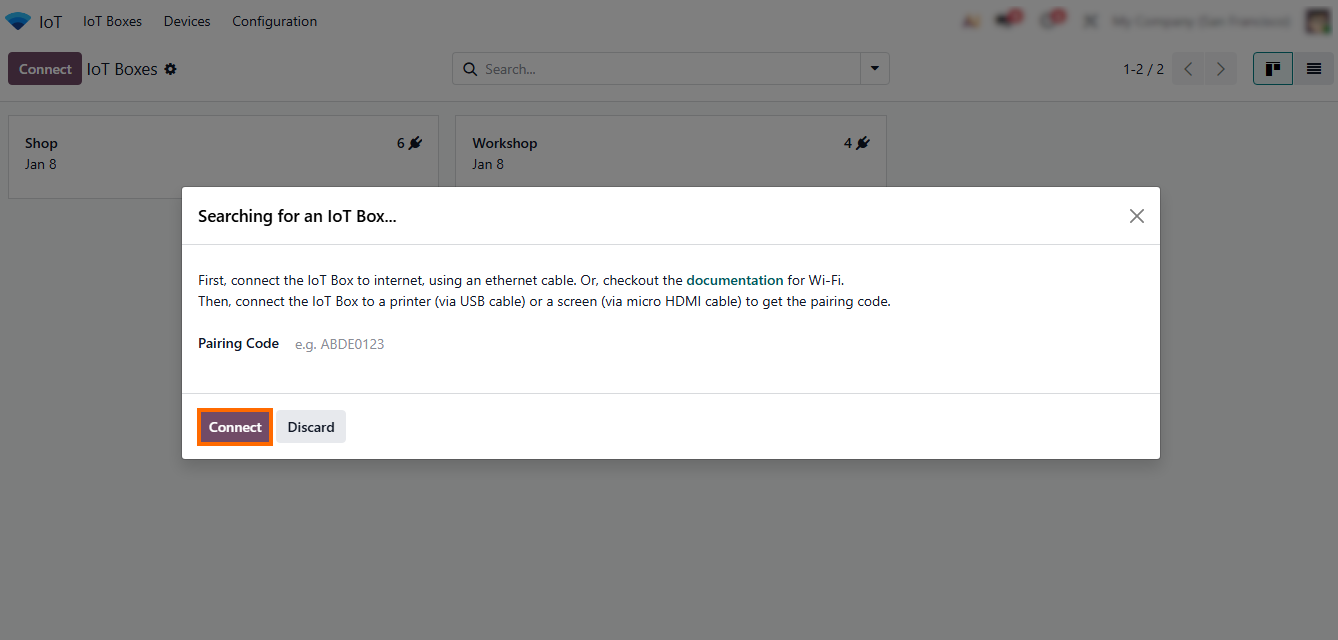
- If “Use Pairing Code” is selected, enter the device’s unique code and confirm. Once paired, it appears in the IoT Boxes list, ready for workflow assignment and use in Odoo 19.
IoT in a Box in Odoo 19: Practical Management of Odoo
IoT Box and IoT Boxes
Once your device is paired, it can be managed directly from the Odoo IoT Box interface, where all IoT boxes and peripherals are listed for daily control and monitoring. Connected devices enable real-time interaction with Odoo IoT workflows using Odoo wireless communication, making operations faster and reducing manual errors. By assigning devices from the Odoo IoTBox or IoTBox Odoo environment to specific modules like Inventory, Manufacturing, or POS, businesses ensure that physical actions are immediately reflected in the ERP system. In this IoT in a box architecture, the box IoT component only transfers signals, while business logic remains inside IoT Odoo applications.
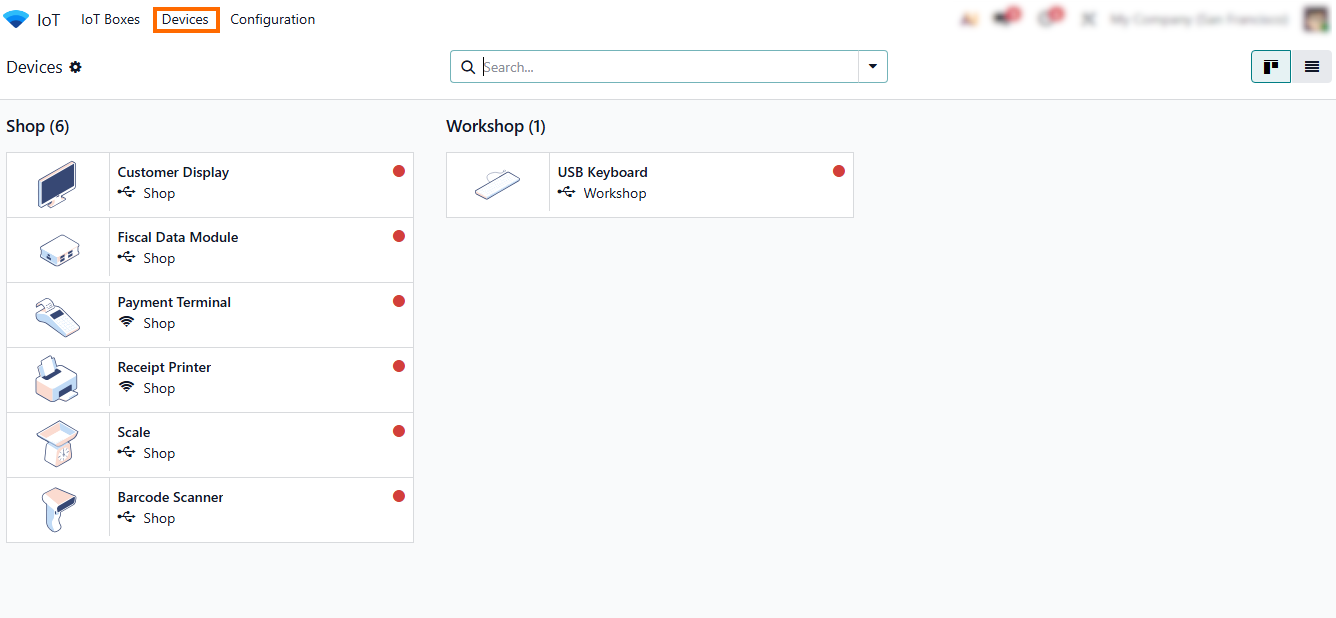
- The connected device is now listed as “Workshop”. This confirms that the pairing process with the Odoo IoT Box was successful and the device is ready for configuration.

- Click “Device”to open the device card, where you can view its details, configure settings, assign it to a workflow, or run basic functionality tests.
- You can also edit device settings to change the workflow it interacts with, rename the device for easier identification, or remove it if it is no longer needed.
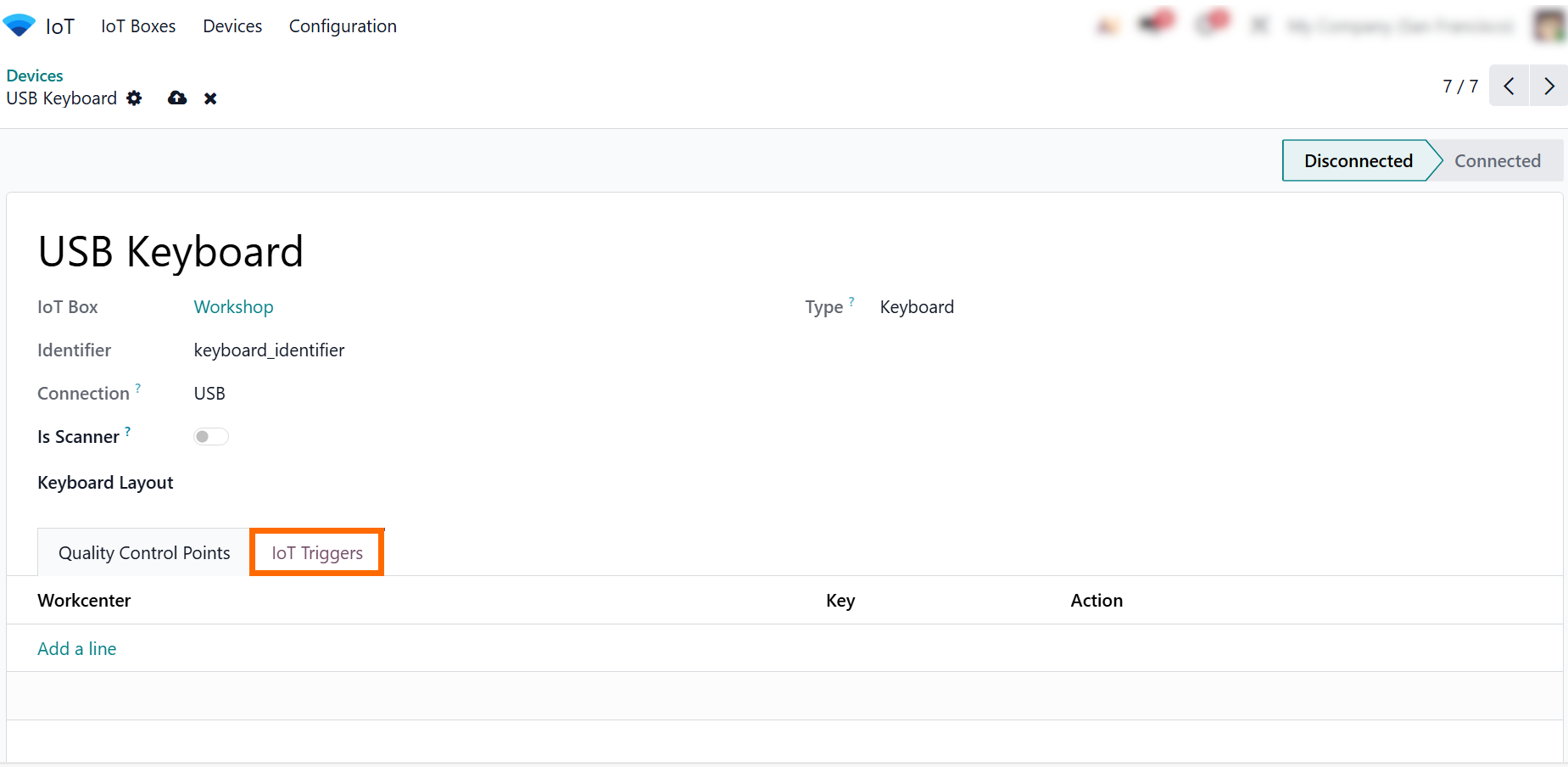
- Click “IoT Triggers” to configure actions for the device. Define which Odoo workflows are triggered by events like button presses, scans, or scale measurements.
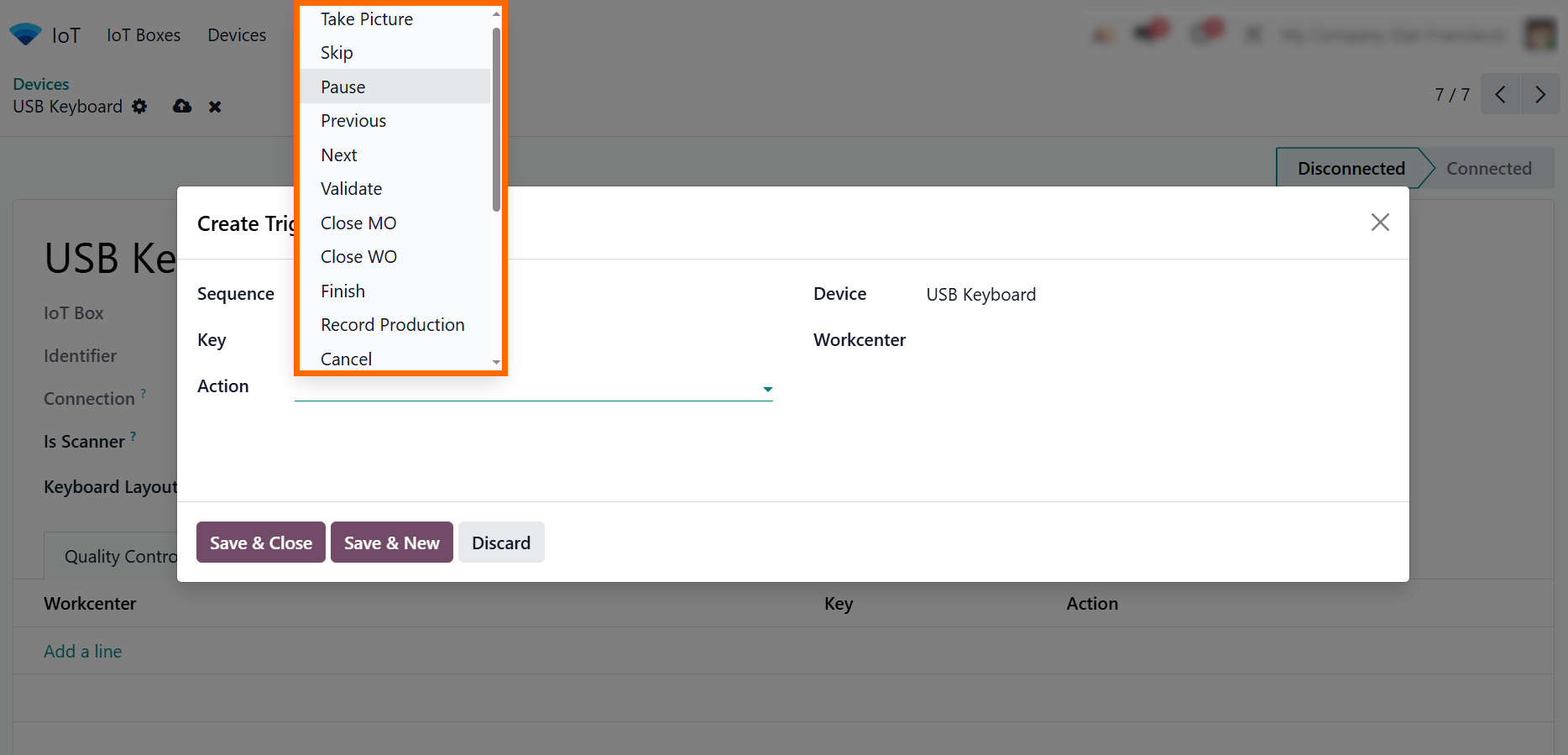
- Select the “Work Center”, “Action”, or “document type” that should receive the device signal, depending on the application where the device is used.
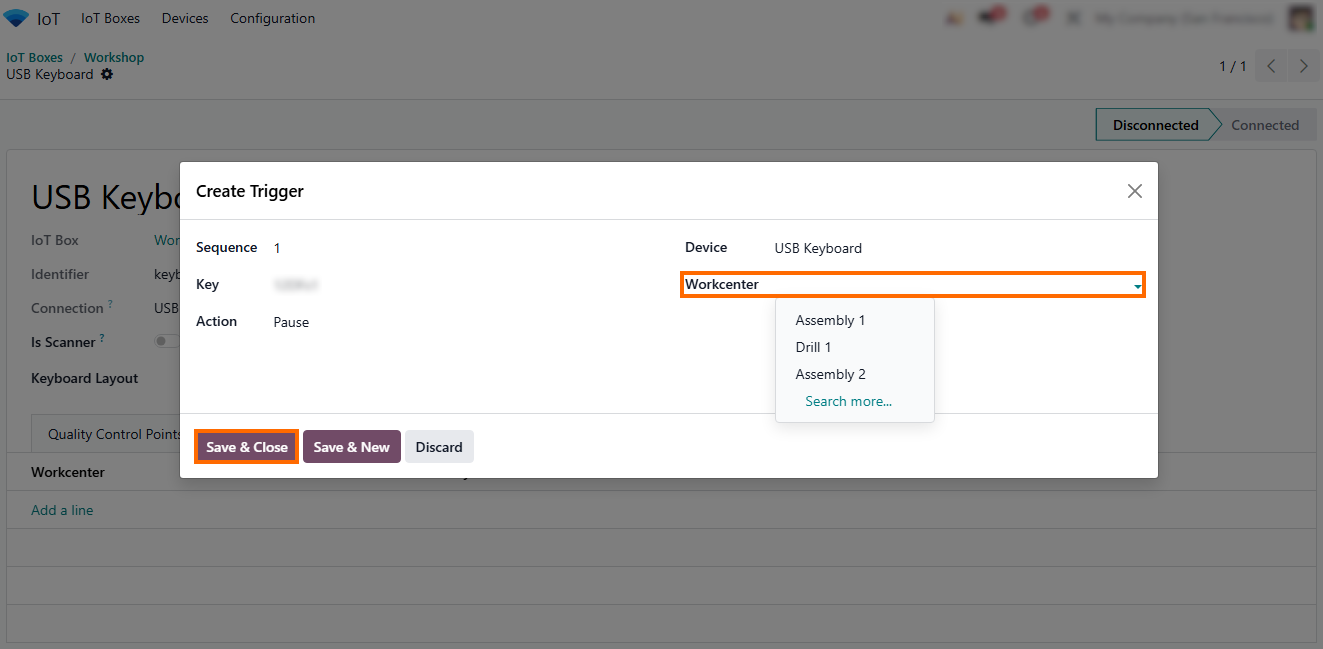
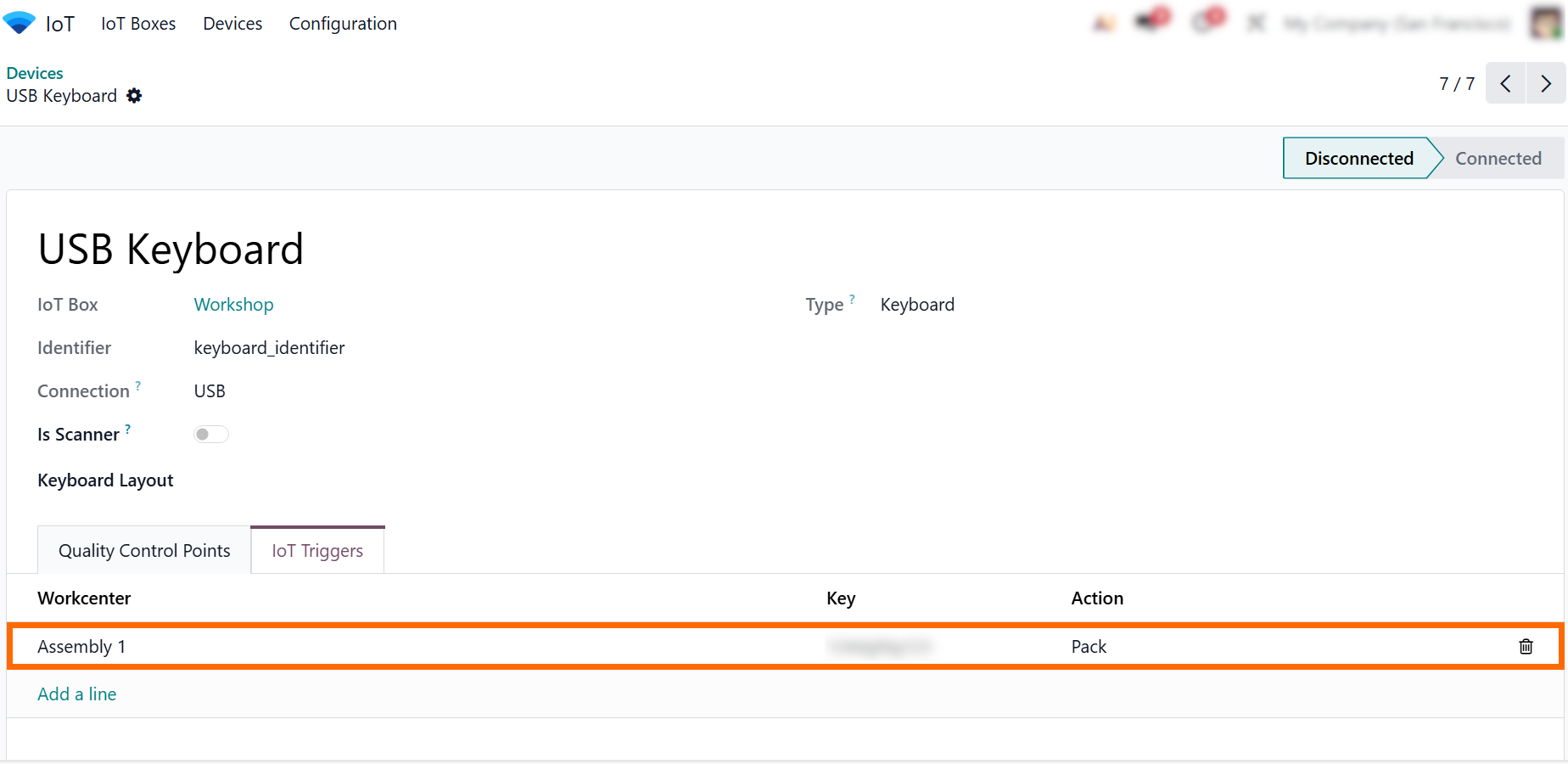
- After adding an IoT
trigger, it will appear in the trigger list, where it can be reviewed, edited,
or extended as workflows evolve and business processes change.
Managing IoT Devices in Manufacturing Through Work Centers and Odoo IoT Box
In manufacturing environments, most daily interactions with connected devices are managed directly through Work Centers rather than general system settings. When devices are paired using the Odoo IoT Box, Odoo IoTBox, or IoTBox Odoo, they become available inside production Work Centers, where operational actions are defined. This approach keeps IoT in a box deployments tightly aligned with real production workflows instead of isolated device management screens. The Odoo box and other IoT boxes function as communication hubs, while all business logic remains inside IoT Odoo applications and manufacturing operations using Odoo wireless connectivity, allowing operators and managers to control, monitor, and assign device-triggered actions directly within the production environment.
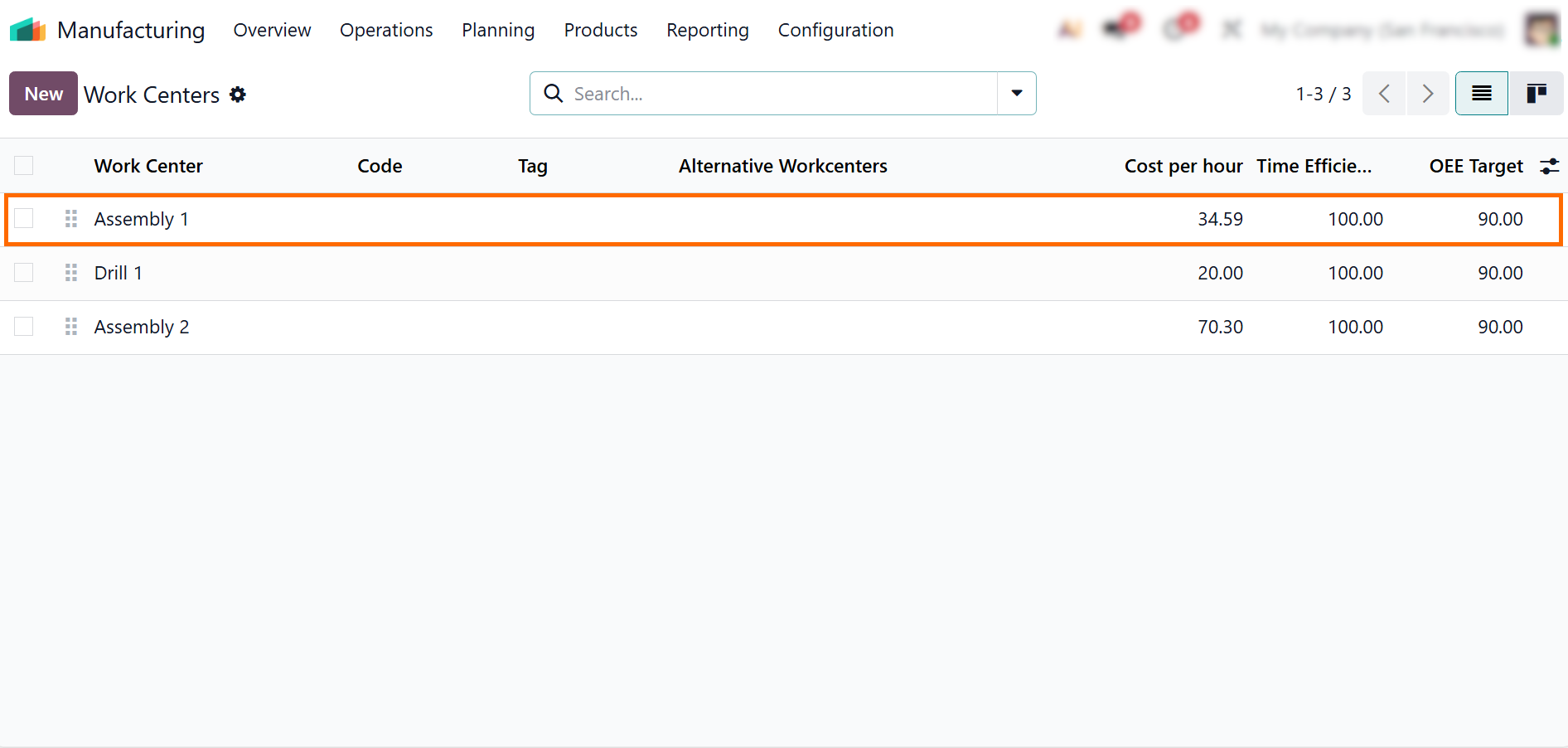
- To link a device to production activities, navigate to “Manufacturing”, open “Configuration”, and select “Work Centers”, then open the required work center.
- Select the relevant work center and review its operational settings, including capacity, working hours, and connected devices, to ensure that IoT actions are applied to the correct production stage.
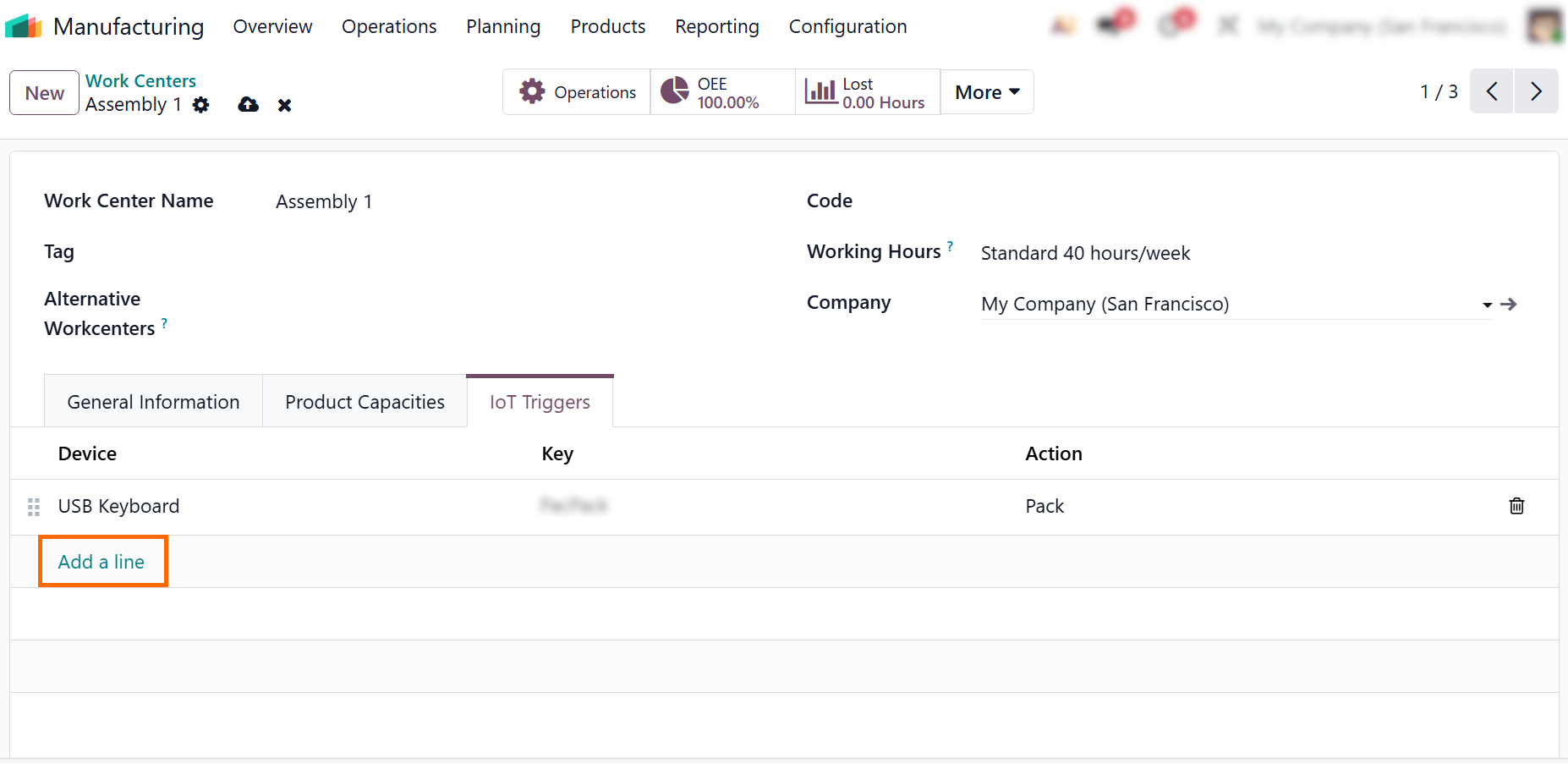
- Use the “IoT Triggers” tab to assign connected hardware from the IoT in a Box – “My Devices” list and define which device events should trigger actions within the selected production workflow.
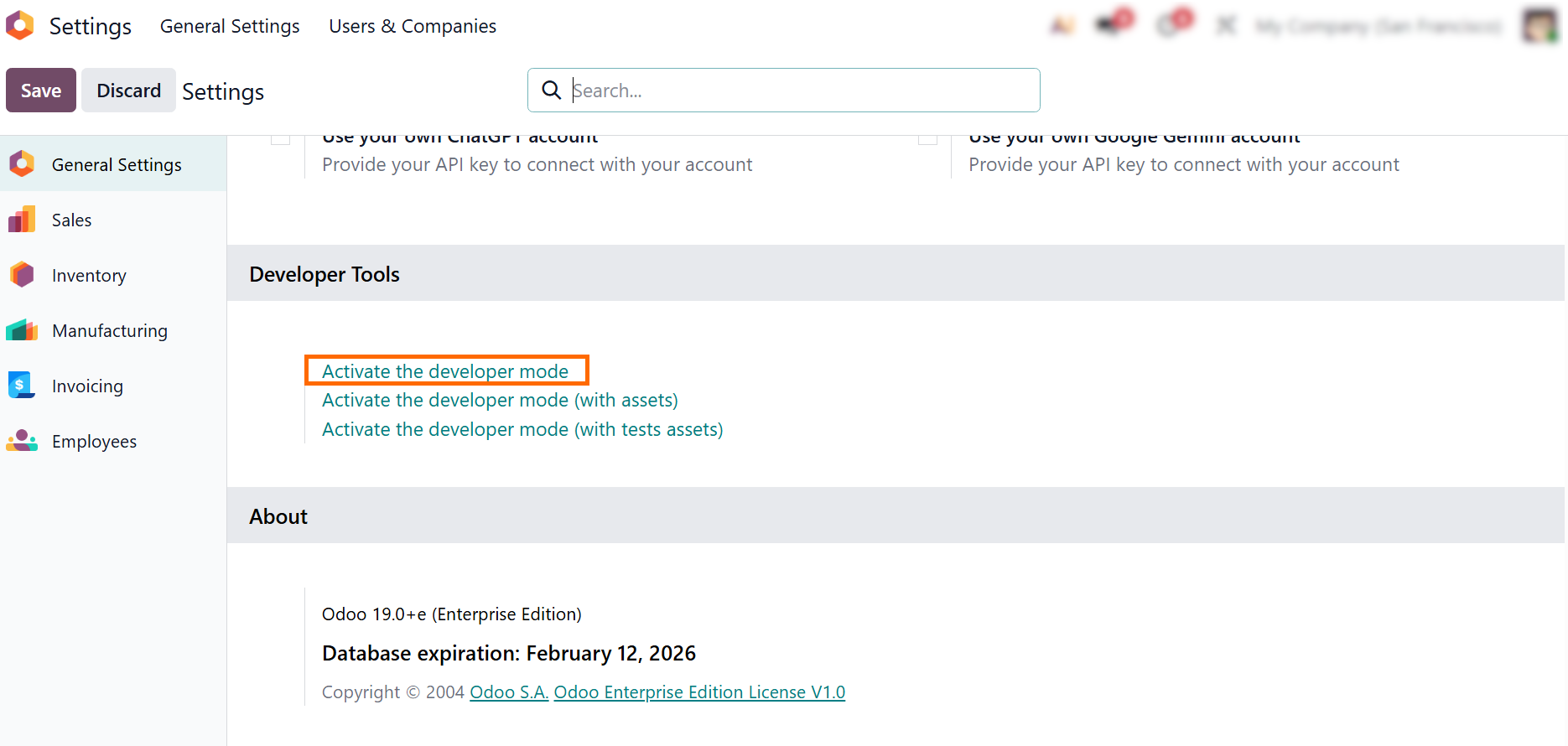
- When standard IoT actions are not sufficient, device behavior can be extended through custom development to support specific production or quality scenarios.
Odoo IoT Box in Action: Practical Use Cases Across Business Operations
While the Odoo IoT Box functions as a technical bridge between physical devices and the ERP system, its real value becomes clear in daily operational scenarios. By using IoT in a box setups, companies can connect scanners, buttons, scales, and printers to Odoo workflows, turning manual actions into structured system events. With Odoo IoTBox and multiple IoT boxes deployed across workstations, physical processes become part of standard ERP-controlled operations, supported by Odoo wireless connectivity and centralized device management. The following practical cases illustrate how IoTBox Odoo and Odoo IoT integrations support core business functions across Manufacturing, Quality, Inventory, and Point of Sale environments.
Manufacturing Operations with IoT Box Odoo and Work Center Triggers
In manufacturing, the Odoo IoT Box is often used to confirm work orders and operations directly from the shop floor. By connecting physical buttons or barcode scanners through Odoo IoT boxes, operators can validate production steps without using keyboards or terminals. A simple device signal sent by the IoT box Odoo can confirm an operation, register output quantities, or trigger the next workflow step. All routing logic and validations remain inside Odoo Manufacturing, while the box IoT layer only transmits device signals. Odoo IoT Box turns manual production confirmations into instant, error-free updates with real-time workflow visibility.
Quality Control Automation Using IoT in a Box and Odoo IoTBox
Quality teams use IoT in a box setups to trigger inspections and approvals directly from physical workstations, using measurement devices or approval buttons connected via the IoT Box. Device availability and connectivity can be monitored through IoT in a Box – My Devices, allowing supervisors to quickly detect offline IoT boxes. In some deployments, extended monitoring and cloud services may require an active IoT subscription, especially when managing distributed sites. This ensures stable IoT Odoo operations while keeping business logic fully inside ERP workflows.
Inventory and Warehouse Processes with Odoo IoT Boxes and Odoo Wireless Devices
In warehouse operations, Odoo IoT Box integrations simplify picking, packing, and receiving workflows. Barcode scanners and scales connected via Odoo IoT boxes automatically update stock moves and quantities in Odoo Inventory, reducing manual corrections and delays. Multiple IoT boxes can be deployed in different warehouse zones, each acting as an Odoo box gateway for local devices. With Odoo wireless connectivity, devices can be replaced or relocated without reconfiguration, while Odoo IoT ensures that all inventory validations and tracking remain centralized in the ERP system.
Point of Sale Automation with Odoo Box and IoT Odoo Integration
In retail environments, the Odoo box connects receipt printers, barcode scanners, cash drawers, and customer displays to POS workflows using IoTBox Odoo. When a sale is confirmed, the Odoo IoT Box automatically triggers printing and drawer actions, eliminating manual handling of checkout devices. Using IoT in a box configurations, stores can deploy multiple IoT boxes per location to support several terminals. Odoo wireless device connectivity allows flexible store layouts, while IoT Odoo keeps all transaction logic and fiscal controls inside the POS application.
Conclusion
The Odoo IoT Box and Odoo IoTBox redefine how modern companies integrate physical devices into ERP workflows. As an IoT in a box solution, it goes far beyond basic device connectivity, transforming signals from scanners, scales, buttons, and other equipment into structured actions inside Odoo IoT applications. Whether teams manage Manufacturing, Quality, Inventory, or POS operations, IoTBox Odoo ensures that every physical interaction is accurately recorded and processed within the ERP system.
With Odoo wireless connectivity, centralized monitoring through IoT in a Box – My Devices, and optional IoT subscription services, businesses gain full visibility into device availability and performance across locations. Using distributed IoT boxes and localized box IoT setups, workstations communicate directly with Odoo in real time, reducing manual input, minimizing operational errors, and keeping workflows consistent across departments.
The broader Odoo Box ecosystem enables companies to build a scalable and fully integrated device management layer directly inside their ERP. By consolidating hardware interactions within the Odoo IoT Box framework, organizations establish reliable foundations for real-time execution, operational transparency, and continuous process optimization. From production lines to warehouse zones and retail terminals, Odoo IoTBox supports connected business operations where physical work and digital control function as a single system.