
Shift Left Testing concept – Benefits and Why is it Necessary? | KoderShop

Shift Left Testing
The software development lifecycle must incorporate quicker and earlier testing due to the nearly universal use of agile methodologies (SDLC). ‘Shifting left’.is a term used to describe early integration of development and testing.
You might be asking what I mean when I say “Shift Left” while I’m talking about the program.
When I began my career as a software tester more than two decades ago, there was no such thing as a “Testing Phase” for software development, and the role of the tester didn’t even exist. Developers used to create software and test it.
When production errors began to affect the project’s budget, the idea of software testing was progressively introduced, and “Functional Testing” was implemented with a relatively small team of testers. We were only two Testers compared to a group of 20 Developers at that time.
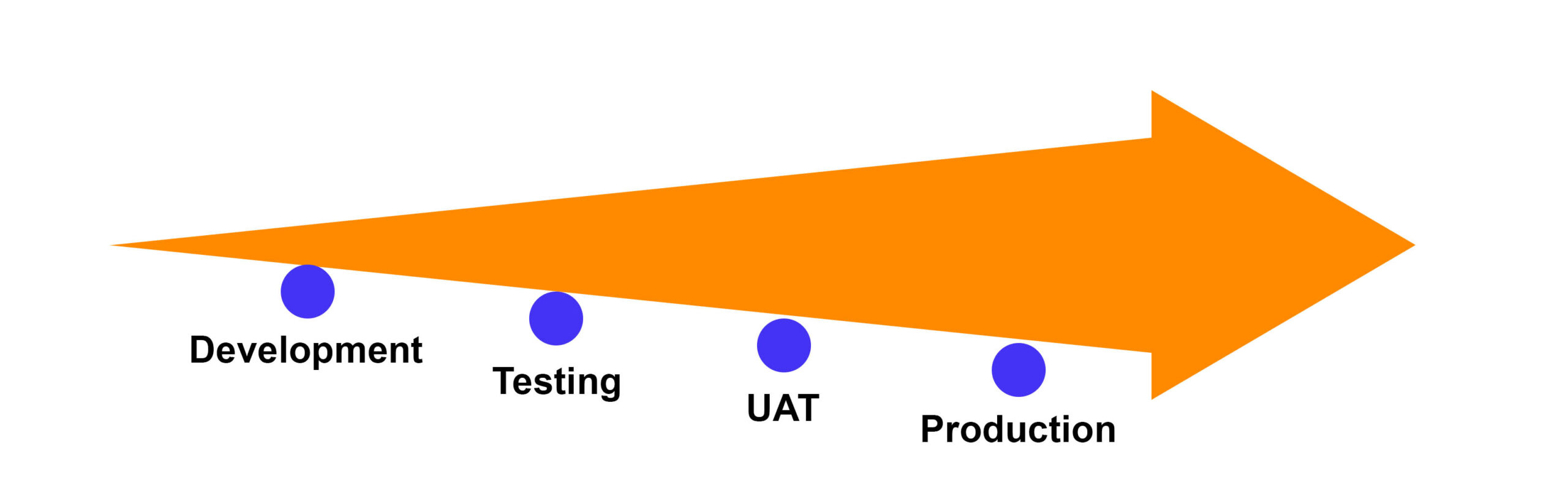
Since the software development lifecycle is known to proceed sequentially in the sequence of, the IT industry has begun utilizing the waterfall model like Requirements => Design => Coding => Testing.
Traditional testing
The testing would have taken place right before the software was released into production in a conventional waterfall software development process. This implied that the release would be postponed until any bugs or usability problems were resolved.
In this scenario, testing turned into a bottleneck that substantially hampered projects’ ability to finish on schedule.
Introduction to the Shift Left Concept
Over time, individuals came to understand the value of software testing and the consequences of maintaining the “Testing Phase” at the very end or on the extreme right of the software development lifecycle. This epiphany was brought on by the fact that fixing the bugs at the very end and far right were exceedingly expensive, time-consuming, and labor-intensive.
There have been instances where, despite putting in a lot of time and effort, the mission-essential software was unable to be launched to the market because of a critical bug that was discovered only at the very end.
As a result, because the fault was discovered in the final stages of development, either the release was postponed or, in some cases, the software was abandoned because fixing the bug would have required too much work.
There is a great quote about testing: “Defects are less costly when caught early.”
This insight and the important lesson learnt sparked a significant change in the software industry and gave rise to the idea of “Shift Left,” which refers to moving the “Testing Phase” from the right to the left or incorporating testing at every stage and involving testers all the way through.
Shift Left testing also refers to the practice of conducting ongoing tests rather than final ones.
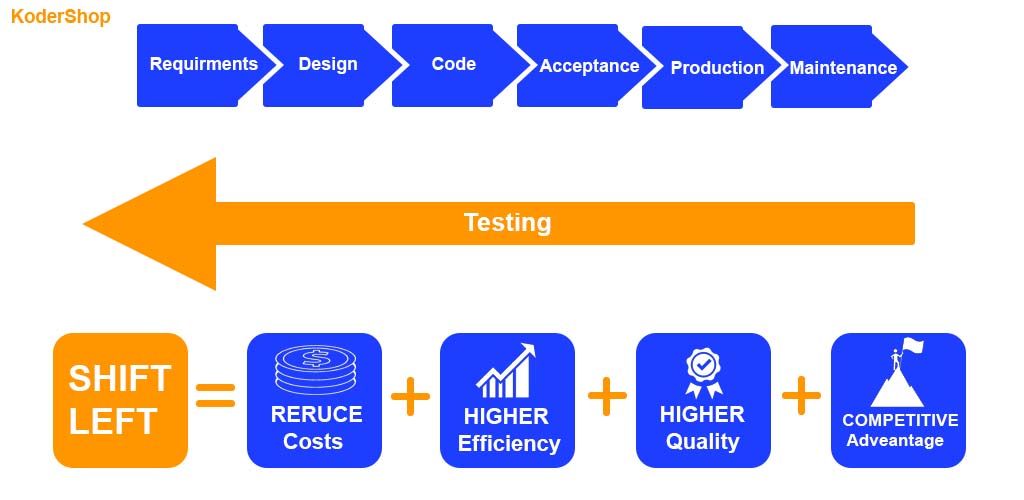
What is Shift Left Testing?
First off, the “Shift left” idea encourages early collaboration between the Testing team and all other stakeholders. As a result, they are able to easily comprehend the specifications and create test cases that will assist the program “Fail Fast” and provide the team the opportunity to address any issues as soon as possible.
The Shift Left approach entails including testers much earlier in the software development life cycle, allowing them to better comprehend requirements, software design, architecture, coding, and functionality. They would also be able to ask challenging questions of customers, business analysts, and developers, get clarifications, and offer feedback whenever it is helpful to the team.
This engagement and comprehension will encourage the testers to learn everything there is to know about the product, consider various scenarios, and create real-world scenarios based on software behavior, all of which will aid the team in finding bugs even before any coding has been done.
Why Shift Left testing?
The delivery and testing requirements are retained on the right side of the plan in the traditional software development paradigm, while the requirements are kept on the left. The issue is that these procedures can’t adapt to shifting standards and specifications, which has detrimental effects on the company’s operations, including:
- Increased costs
- longer time to market
- Unexpected mistakes
Cost is a very powerful motivator for moving your testing to the left. According to estimates, less than 10% of software problems appear during the lifecycle’s development phase, and more than half of all defects could be found during the requirements phase. The cost of fixing these flaws works backwards:
The cost to find and fix a flaw after the product has been released will be roughly 100 times higher than during the requirements phase. According to research from the Ponemon Institute published in 2017, vulnerabilities may cost an average of $80 to fix if they are discovered during the early stages of development. But the same vulnerabilities may cost roughly $7,600 to repair if found after they have moved into production.
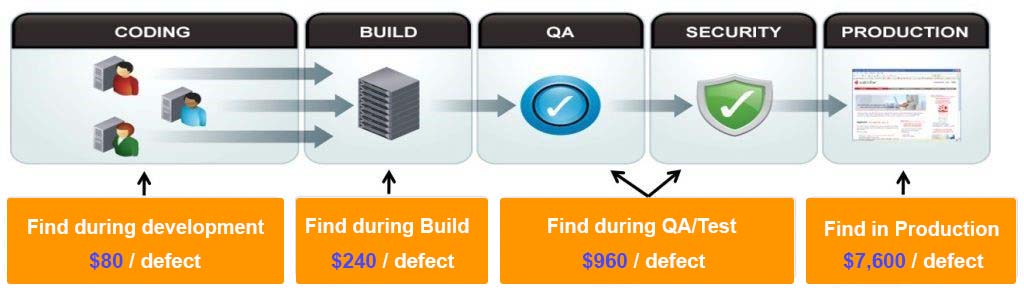
The Shifting Left methodology emphasizes the necessity for developers to focus on quality from the beginning of a software build rather than waiting until faults and issues are discovered toward the end of the SDLC. Product teams can complete routine tasks such as:
- Testing
- Feedback
- Reviewing all of changes and the progress made
How Does Shift Left Influence Software Development?
The Shift Left method is centered on including testers in all, but especially in the crucial phases of the program. As a result, the testers may shift their attention from problem discovery to defect prevention and help the program achieve its business objectives.
The shift Left strategy gives testing a high priority, which greatly expands the duties and responsibilities of testers.
As the testing team’s responsibilities grow, the team actively collaborates with the team from the start to plan and develop a robust and effective testing strategy. This is done by offering the team excellent test leadership and guidance and focusing on the long-term vision of the product rather than just taking on the responsibility of the testing work. The Shift Left methodology allows the testers the chance to design the tests first, where the tests are entirely focused on the customer experience and their expectations, allowing the developers to build the software based on these tests and so satisfy the needs of the customers.
The Testers are not the only ones affected by the Shift Left strategy. The Developers will be able to take greater ownership of their code and assume more responsibility for testing by moving to the let and doing the testing activities consistently. The shift Left approach also encourages testers to use test-driven development (TDD) and behavioral driven development (BDD), which helps to stop software defects from being introduced. Agile Shift Left Testing: The Shift Left methodology encourages the creation of Agile Scrum Teams that must include testers along with all other roles. Testers are also included in regular stand-up calls, other interactions, and review meetings, which has given them access to additional program-related knowledge.
Is Shift Left approach in testing always appropriate?
It’s possible that a Shift Left testing strategy won’t always be able to produce the best performance and functioning in a real-world setting. In certain circumstances, a Shift Right testing approach may be used to:
- Increase client satisfaction
- Give direction for implementing test automation
- Better test coverage is ensured
Testing is started by Shift Right from the right, i.e. post-production. To ensure performance and usability, you’ll test a fully developed and operational application in this Shift Right exercise. Reviews and comments from targeted users also contribute to improving the software’s quality.
An essential component of the Shift Right strategy is a readiness to:
- Test a theory’ veracity by implementing fresh ideas
- Work together with customers to figure out what is effective (instead of working from assumptions)
Users’ ongoing feedback could improve how we react to software faults.
Shift Left Techniques
You may shift left with your software testing by using a few important strategies:
Demand planning
With a forward-looking view of demand, test analysts will interact with business and operational stakeholders. With this perspective, you may plan and decide in advance:
- Budget
- Resourcing
- Strategies on testing
Demand planning is a crucial component of the shift left strategy and serves as the foundation for all other test lifecycle tasks.
Static testing
Early on in the project’s lifecycles, requirements and designs are validated as part of static testing. Static testing’s goal is to identify flaws early in a product’s life cycle before they become highly expensive to fix in the project’s later stages.
Utilize the proper checklists to validate the requirements and design. Enter errors in a tool for defect management.
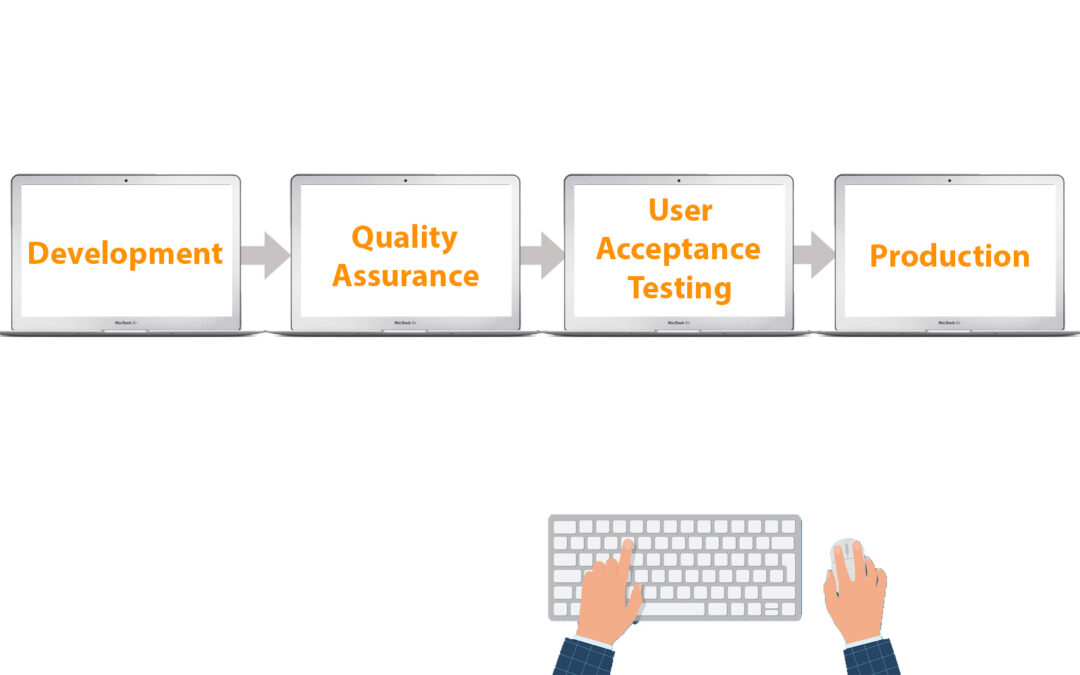
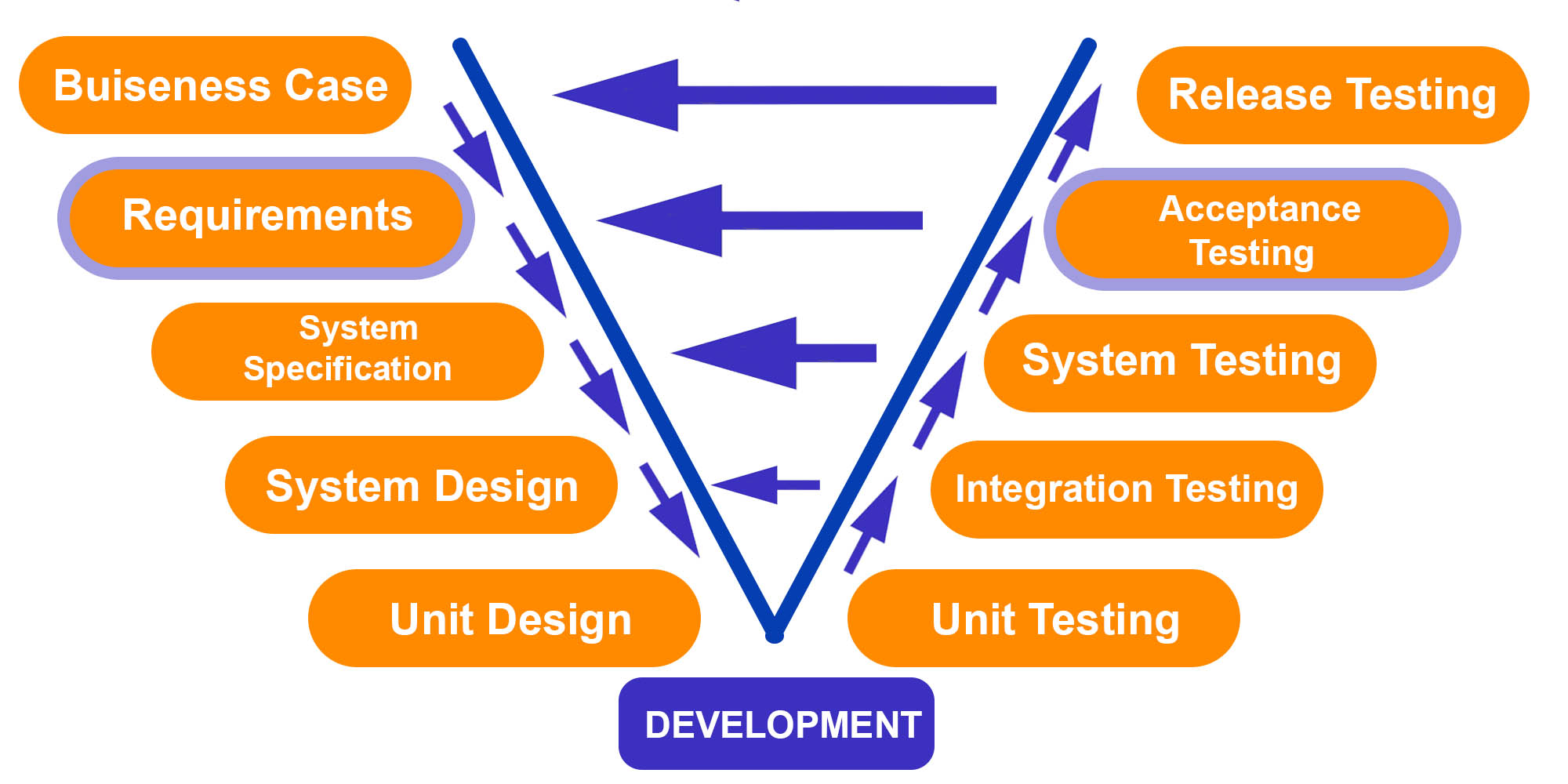
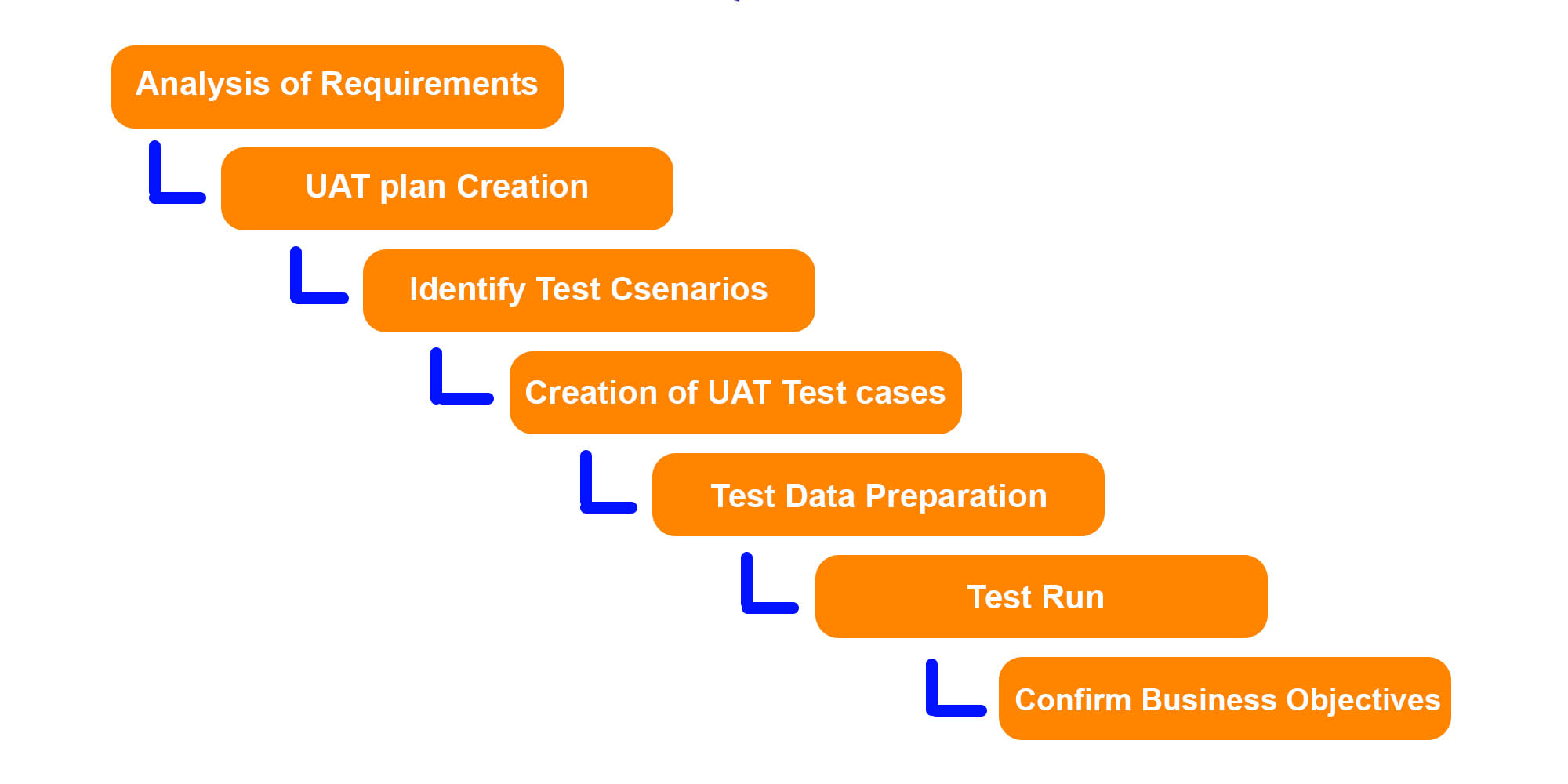
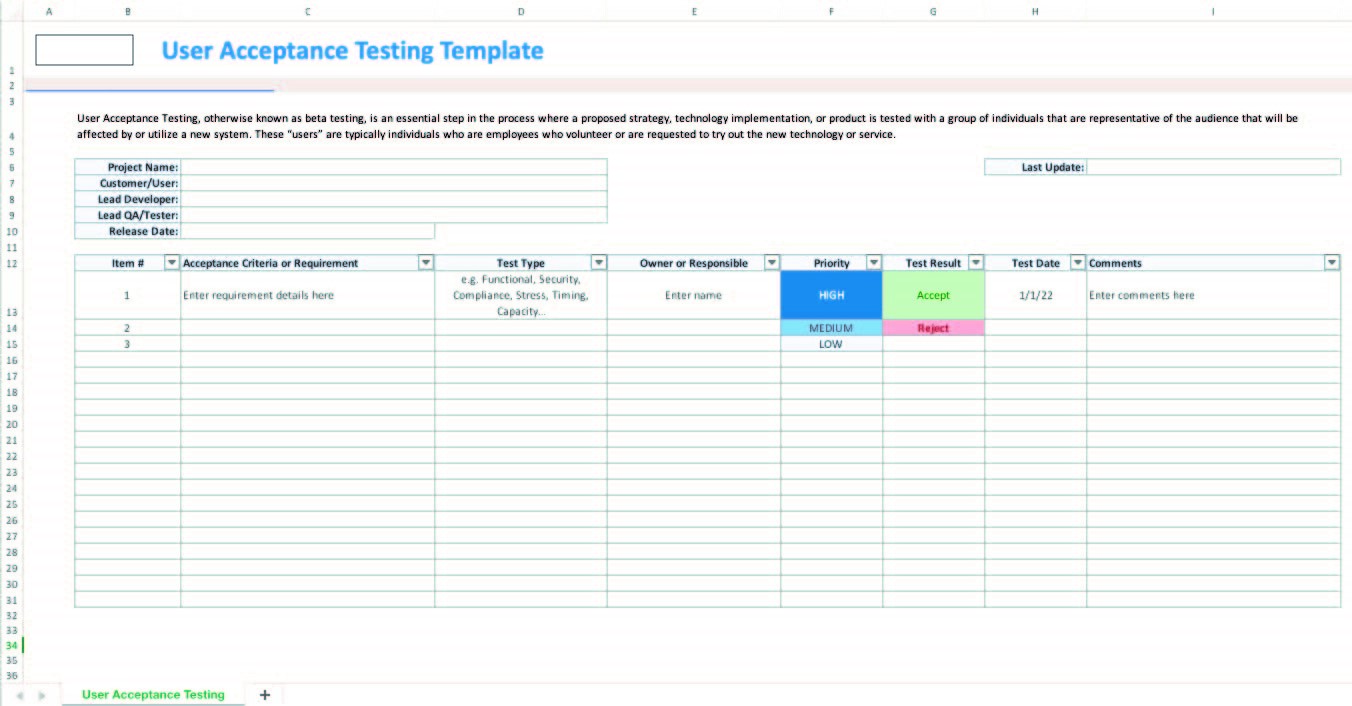
Unified test strategy
This is a comprehensive, high-level testing method that covers end-to-end testing from unit testing to operational readiness testing (ORT), user acceptance testing (UAT), and post-deployment testing. The plan will outline precise roles for each stage of quality control.
By analyzing dependencies on environments, stubs, automation, and test results, you can make sure that the various teams can meet the demands.
Analysis based on risk
For each test scenario, a risk-based analysis is done to estimate the consequences and chance of failure. Functional, non-functional, and regression testing all employ this methodology.
After the test cases are created, rank them in order of importance using the results of the analysis. With the business analyst or designer, go over the consequences of failure. From the development team, ascertain the risk of failure.
Shift Left Testing process is:
- Early fault detection helps keep the project’s cost down.
- Testing continually, repeatedly, and finally reduces defects
- To accelerate time to market and automate everything.
- To concentrate on customer needs and enhance the client experience.
Benefits of shift left approach
A shift left strategy has a number of advantages that can be attained. Some of the most crucial are listed below:
Automation
Testing can be automated more effectively by shifting to the left. These important advantages of test automation are offered:
- Less human errors
- more thorough test coverage (multiple tests can be conducted at the same time)
- the capacity for testers to concentrate on more engaging and rewarding activities
- less production problems
Accelerated delivery
Faster is earlier. Defects are much easier to rectify when discovered early in the production cycle. The result is:
- The interval between releases may shorten dramatically.
- The software gets better in quality.
Increased contentment
One of the main advantages of the shift-left strategy is faster delivery of software with fewer flaws.
The looks on your business associates’ faces should be enough to persuade you that this is a smart choice if nothing else.
To increase their velocity, quality, and efficiency, Humana chose a contemporary mainframe development environment for editing and debugging code.
Conclusion
The entire “Testing” job underwent a significant alteration as a result of the “Shift Left” concept. Up until that point, the main goal of testing was “Defect Detection,” but now the goal of the “Shift Left” is a trip from “Early Defect Detection to Static Testing.”
As a result, Shift Left represents a Big Leap in the Software Development technique for the software industry in terms of accelerating time to market, enhancing software quality, and decreasing “Time to Market.”


Recent Comments